You’re standing in the grocery store, comparing the nutrition information for two different cereals. The enriched wheat bran cereal has more B12 vitamin content than your favorite sugary one. As an adult, you know that your body needs the additional vitamins in the enriched bran flakes, even if you really want that fruity, sugary hit in the morning.
In security, your data needs that additional hit of nutrition so you can correlate and analyze events more effectively. For data, enrichment means adding context to raw data, enabling you to gain insights and reduce alert fatigue.
To understand the value of data enrichment for cybersecurity, you should understand what data enrichment is, how your security solutions implement it, and how it improves threat detection and incident response.
What is Data Enrichment?
Data enrichment is a process that enhances raw information by adding valuable details from various external sources. In cybersecurity, this means combining security event data with other relevant information, including context about:
- Users, like geographic location or access privileges
- Devices like operating systems or software
- Data types like personally identifiable information (PII), protected health information (PHI), or cardholder data
(Possible redaction of this data for privacy purposes)
When security teams can add this context to their security monitoring, they can correlate data more precisely to improve alert fidelity and reduce alert fatigue. For example, enriching security telemetry data can improve:
- Threat detections by incorporating threat intelligence to look for indicators of compromise and known attack tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs)
- Incident response times by using the context to narrow down an incident’s root cause
- Risk management by using context to improve anomaly detection analytics models
By continuously updating and enriching data, you can keep pace with the evolving threat landscape. For example, enriching a user’s access data with their geographic location enables your security team to identify potentially compromised credentials when the user logs into the network from a suspicious IP address or location.
Types of Cybersecurity Data Enrichment
Your organization’s enterprise IT technologies and cybersecurity tools all generate log data that helps you understand your security posture. Some examples of this data include:
- Login failures and successes
- Inbound and outbound network traffic
- Asset and Vulnerability Scan Reports
- API calls
While this information will tell you some of what’s happening, data enrichment provides deeper insights. Some additional context for cybersecurity data may include:
- Threat Intelligence: Data about indicators of compromise from external sources like threat intelligence feeds, helping detect genuine threats.
- Geolocation: Location data for IP addresses that can aid in identifying potential security threats from specific regions.
- Historical Data: Data from past security incidents to help distinguish false positives from real threats.
- Vulnerability Enrichment: Vulnerability database information that highlights potential security threats tied to known security weaknesses.
3 Benefits of Enriching Cybersecurity Data
By adding more context to your security data, your security team can gain better insights into potential threats and mitigate risk more effectively.
1. Improved Threat Detection
Analytics models thrive on data. When you add context to your log data, your security analytics models gain a better understanding of the normal, baseline activity across your users and IT environment. Data enrichment also allows your security team to create high-fidelity alerts to reduce false positives.
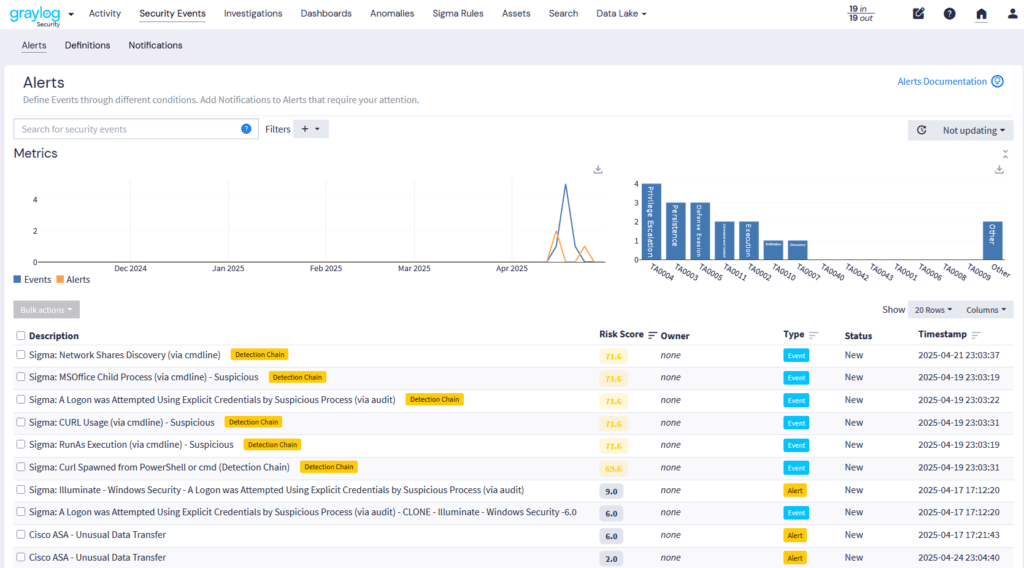
2. Improved Incident Response
Data enrichment improves key investigation and response metrics, like mean time to contain (MTTC) and mean time to resolve (MTTR). Your threat detection and incident response (TDIR) solution can use this context to help generate an incident timeline that helps your security team trace the attacker.
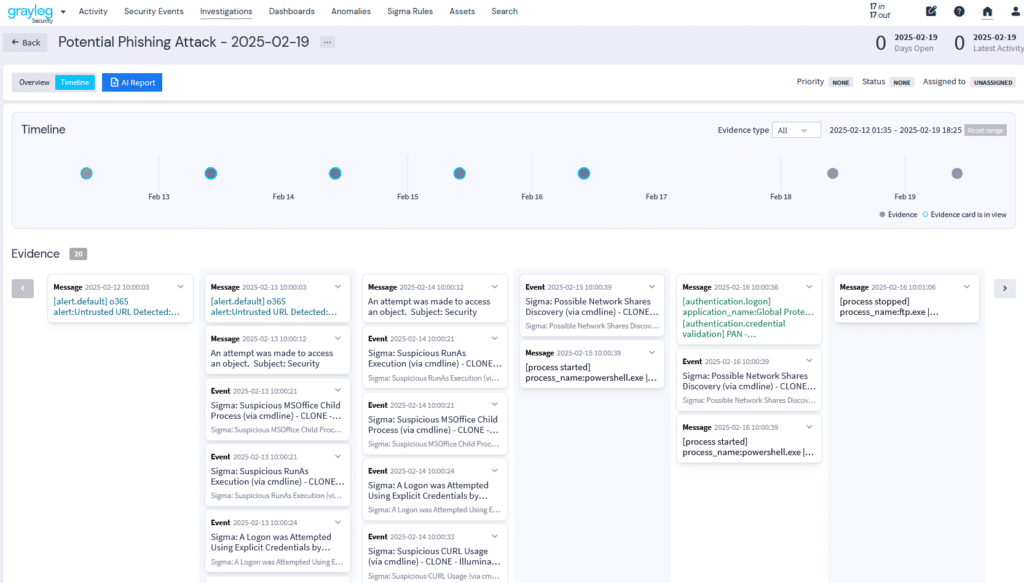
3. Reduced Storage Costs
Adding context means having all your data in a centralized location. Many organizations store their telemetry in a security data lake. When you parse and enrich the data before sending it to the data lake, you can leverage the less expensive storage solution while still having data ready for an investigation if you need it.
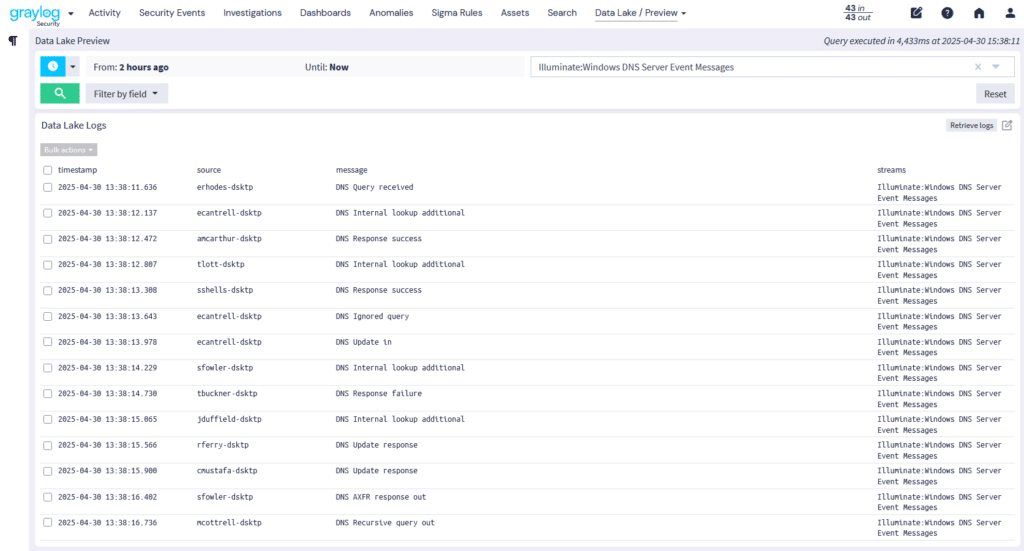
Best Practices for Enriching and Using Cybersecurity Data
Data enrichment in cybersecurity aids your security team so they can more effectively detect and respond to potential security incidents. To achieve the full benefits of your security data, you can follow these best practices.
Centralize All Security Data.
Combining log data from across your environment is the first step to enrichment. By integrating data from your IT and security technologies in a centralized location, you can correlate and analyze events from across the environment to improve your threat detection capabilities and respond to potential incidents faster.
Normalize and Parse Security Telemetry
As part of enriching your data, you need everything to be in a common, structured format. The parsing and normalization process takes out the important parts of your logs and standardizes their format so that you can make connections between events to gain real-time insights.
Integrate Threat Intelligence
Integrating threat intelligence feeds allows organizations to detect potential threats before malicious actors can gain unauthorized access to sensitive data. Enriching your data with threat intelligence enables your response team to build high-fidelity detections that reduce alert fatigue by reducing false positives.
Enrich Data En-route to Storage
If you use a security data lake, you reduce storage costs. However, you may still need this data during an investigation. You should add the context inside the data before sending it to the storage repository so that when you want to search it, you have parsed and normalized data ready.
Simplify Data Handling
While you want to collect and enrich all data, you may not need everything immediately. To use your enriched data effectively and efficiently, you should implement a data management solution so you can separate out:
- Active data used in real-time for dashboards, event alerts, and anomaly detection
- Warm data used occasionally, like operational logs, historical IT performance metrics, or past event logs that may support troubleshooting or retrospective analysis
- Archivable data stored for long-term compliance and historical analysis purposes
Leverage Analytics
Once you enrich your data, you can integrate analytics that help you identify anomalous activity that could be a potential security incident. With distributed, remote workforces, malicious actors increasingly use stolen or leaked credentials to gain unauthorized access. Anomaly detection analytics define your environment’s baseline normal using enriched data to combine user credentials and access permissions with geographic location and other information to identify potential threats.
Graylog: Data Enrichment for Cybersecurity Data
Graylog’s data enrichment capabilities enable you to incorporate valuable context to existing logs and security events to help enhance your security operations. Our solution integrates different types of contextual information, including user identity, geographic location, and device specifications. We enrich data during the parsing and normalization process so that it contains the context no matter where you store it initially.
With this enriched data, you can improve risk scoring, readability, search, and data visualization for a cohesive analysis offering comprehensive insights into your systems performance and security.
To see how Graylog fits into your organization’s security and IT operations strategy, contact us today.