Gamers of a certain age likely remember the video game Asteroids. You played as a little triangular spacecraft shooting at big space rocks that started traveling towards you slowly at first, then gained speed. As you revolved around trying to protect yourself by shooting them, you inevitably had to make some rapid decisions about which asteroids would harm your ship the most and which ones you could potentially ignore.
In cybersecurity, you do the same thing when trying to triage alerts. Just like not all asteroids would cause the same amount of damage to your ship, not all incidents have the same impact on systems and data. Triage in cybersecurity is a process that you can use to understand and prioritize threats, so you can more efficiently respond to alerts. When you have a structured approach to triaging incidents, you can appropriately allocate resources during the response process and communicate more effectively with everyone involved.
By centralizing all security activities and leveraging the right technologies, security teams can implement a structured, risk-based approach to triage in incident response that helps them protect systems more effectively.
What is Triage in Cybersecurity?
In cybersecurity, triage is a structured incident prioritization process that accounts for impact and urgency. The process begins with an initial assessment, focusing on severity, potential impact, and escalation likelihood. By implementing a triage process, security teams can investigate and respond to incidents faster, reducing the damage that a security incident can cause.
At a very high level, the triage process looks like this:
- Identify and analyze: quickly review the incident report to evaluate validity
- Incorporate threat intelligence: correlate incident with existing threat intelligence
- Apply predefined criteria: use set standards to determine the incidents that require immediate action
When prioritizing incidents, most organizations use the following three levels:
- High: Respond immediately
- Medium: Handle as soon as possible and review within 24 hours
- Low: Continue monitoring but no urgent action required
How triaging works in the incident response process
Triaging allows you to focus on the threats that can pose the most harm to your organization. As attackers continue to bombard companies with various attack types and methodologies, triaging gives you a way to organize your activities and optimize your response capabilities.
Detect and Report Initial Incident
Effective detections should allow you to identify, analyze, and report on security events by monitoring for abnormal activities across the environment. The initial report should include an overview of what happened and the assets impacted.
Assess and Categorize
In the assessment stage, incidents are evaluated based on impact, urgency, and severity. Once alerted to a potential even, your teams should have a way to assess the potential incident’s:
- Functional Impact: the systems involved and the incident’s effect on business operations
- Information Impact: the effect on data’s confidentiality, integrity, and availability, including potential theft of sensitive information
- Recoverability: incident size and resources impacted to determine the time and resources needed to recover
For example, the categorization of functional impact might look like this:
- None: services remain available to all users
- Low: critical services remain available but may not be delivered efficiently
- Medium: critical services unavailable to a portion of users
- High: critical services unavailable to all users
Prioritize Incidents
The assessment and categorization step allows you to determine an incident’s urgency. Using potential impact and severity as the basic building blocks of your prioritization, you should focus activities on high-priority incidents so you can minimize harm. In theory, prioritization should help your team avoid alert fatigue by allowing you to focus on the most immediate and dangerous incidents.
Assign and Allocate Resources
Each incident’s nature and severity guides resource allocation so that you can have the people with the right skills and experience working on the issue. This structured approach to resource allocation means that you can focus staff and response activities around addressing specific threats or critical systems, minimizing overall incident impact by responding faster.
Start Investigation
During the investigation, you start trying to find the incident’s root cause by gathering data and looking for indicators of compromise (IoCs). As part of this process, you will look for forensic evident that can include data like:
- IP addresses
- User access
- Asset hostnames
- Network traffic
Communicate and Coordinate
To resolve an incident as quickly as possible, you often need to coordinate across different team members and provide updates to impacted users. For example, security teams and network administrators may need to work together to contain a threat by preventing access to or from a specific network segment. With a centralized location for all activities, you can effectively and efficiently inform everyone involved in the incident response process and complete it faster.
What are the challenges of incident response alert triage?
Despite the important role that alert triage plays in mitigating an incident’s impact, many security teams struggle to implement an effective strategy. Some of the main challenges they face include:
- False positives: Alerts lack important context and fail to identify a real security incident.
- Alert fatigue: Chasing down too many false positives causes security teams to tune out alerts or fail to respond to actual incidents.
- Human error risk: Analysts manually prioritizing alerts can make mistakes due to environment and incident complexity.
- Immature data analytics: Machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) models that focus on IoCs can inaccurately prioritize alerts, especially if they are not focused on cybersecurity use cases.
What are the benefits of alert triage?
A security operations center (SOC) gain various benefits when it appropriately triages alerts, including:
- Improved Efficiency: Quickly identifying high-priority incidents among numerous security alerts reduces response times and helps focus on real threats.
- Reduced Alert Fatigue: A structured approach makes it easier to filter out false positives so analysts can concentrate on legitimate, high-priority alerts.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Using indicators of compromise and other threat intelligence gives SOCs context about the alert and an incident’s potential impact for faster assessment and response.
- Proactive Security Posture: Identifying suspicious activity promptly enables security teams to counteract malicious activity before it escalates.
Best Practices for Improving Triage for Incident Response
Alert triage helps your team protect critical assets and respond to potentially harmful incidents faster.
Centralize Security Activities
During an incident, coordinating and communicating across various people and departments is key to a fast, efficient response. When you create a central hub for all security activities, you can assign people the permissions they need to monitor or interact with the investigation. Additionally, with everyone working from the same information, you can document the triage process and incident response activities for compliance purposes.
Use Security-Focused AI/ML
AI/ML can improve your team’s incident response processes, but you should look for analytics models that are purposely trained on cybersecurity use cases. When looking for an anomaly detection solution, you should consider whether it:
- Defined normal activity
- Identified outliers using behavioral analysis
- Sends alerts from the activity deviates from the normal levels
- Provides an anomaly index to generate alerts based on your team’s configurations
Leverage Risk Scores
With risk scoring, you can create a quantitative metric for prioritizing an incident. However, you should consider two different types of risk scores:
- Event: the potential impact to your environment to help decide whether an investigation is necessary
- Asset: the potential impact to a critical assets based on both the event’s risk and any vulnerabilities associated with the assets that make it easier for attackers to complete their objectives
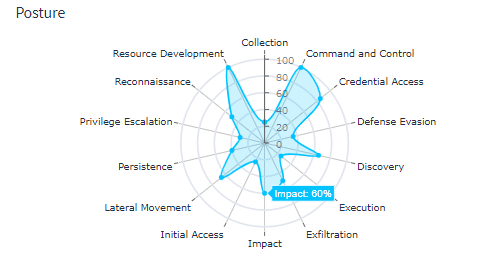
Map Detections to Attack Methods
Your detections, like Sigma rules, help you identify security incidents. When you map detections to threat actor tactics and techniques, you can more accurately understand the potential impact. For example, mapping Sigma rules to the MITRE ATT&CK framework can help you identify high-impact issues based on your current threat coverage without requiring your team to have specialized security skills.
Incorporate Generative AI Purposefully
Generative AI (GenAI) provides a different value than anomaly detection analytics. GenAI models are well-suited to ingesting large amounts of raw data then providing summaries of it. For security teams, this offers a benefit when trying to sort through the log data generated by their environment. When SOCs have a security-focused GenAI tool, they can use the log and event data to generate detailed reports that include key finding and recommended remediation actions.
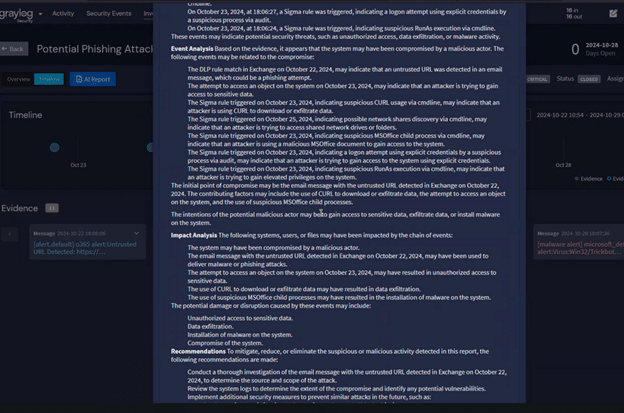
Graylog Security: Risk Scoring and High-Fidelity Alerts to Improve Incident Response
Using Graylog Security, you can rapidly mature your alert triage capabilities. Graylog Security’s Illuminate bundles include rulesets with content that includes Sigma detections, enabling you to uplevel your monitoring by incorporating threat hunting capabilities and correlations to ATT&CK TTPs.
By leveraging our cloud-native capabilities and out-of-the-box content, you gain immediate value from your logs. Our anomaly detection ML improves over time without manual tuning, adapting rapidly to new data sets, organizational priorities, and custom use cases so that you can automate key user and entity access monitoring.
With our intuitive user interface, you can rapidly investigate alerts. Our lightning-fast search capabilities enable you to search terabytes of data in milliseconds, reducing dwell times and shrinking investigations by hours, days, and weeks.
To learn how Graylog Security can help you implement robust threat detection and response, contact us today.