So many logs. So little space. If you’re like most people running an Amazon Web Services (AWS) environment, then you probably have a vast collection of log files that include things like VPC flow logs and CloudWatch data. As if that’s not enough, you’re also collecting information about everything and everyone else connected to your cloud, like users, devices, network devices, applications, and APIs. Recognizing this collection and storage issue, AWS announced their Amazon Security Lake in late 2022 with general availability announced in May 2023.
Amazon Security Lake offers you the cost effective log collection and storage capabilities that you need enabling you to search high volumes of data. However, to optimize the value of your Amazon Security Lake, you still need a solution that provides the correlation and analysis capabilities that allow you to use that data effectively.
What is Amazon Security Lake?
Amazon Security Lake is a way to centralize and store security data generated by:
- AWS environments
- Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) technologies
- On-premises technologies
- Cloud sources
- Third-party sources
Built around Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) buckets, Security Lake gives companies a way to store security-related logs and events as:
- Structured and unstructured data
- Raw and transformed data
Security Lake can collect logs and events generated from AWS services and automatically convert them to the Open Cybersecurity Framework Schema (OCSF). However, users need to convert data from third-party sources to the OCSF schema before sending it.
How Does Amazon Security Lake Work?
When your environment generates logs and events, you can use the application programming interface (API) to send that data to the Security Lake. During this process, Security Lake:
- Runs extract, transform, and load (ETL) on raw data
- Converts data to Apache Parquet
- Converts event fields to OCSF schema
- Stores source data in Amazon S3 buckets in an AWS Account using the region where the data was generated
- Applies a separate prefix to each source in the S3 bucket
- Organizes each source’s data into a separate set of AWS Lake Formation tables
AWS Services
The following natively-supported AWS services include:
- AWS CloudTrail management and data events: history of AWS API calls
- Amazon Route 53 resolver query logs: DNS queries made by resources in the Amazon Virtual Private Cloud
- AWS Security Hub findings: findings from integrations with Amazon services, third-party product integrations, and checks against Security Hub controls
- Amazon VPC Flow Logs: IP traffic going to and from network interfaces
Third-Party Custom Sources
Although you can forward data from third-party custom sources to Security Lake, they must be able to:
- Write data as a set of S3 objects underneath the prefix assigned to the source
- Deliver each unique OCSF event class as a separate source
- Format each S3 object collected as an Apache Parquet file
- Apply each record within a Parquet-formatted object to the same OCSF event class
If your custom sources meet these prerequisites, then Security Lake will handle:
- Providing a unique prefix for the source
- Creating an AWS Identity and Access Management role that permits the source to write data to the data lake
- Creating an AWS Lake Formation table to organize the objects written to the Security Lake
- Establishing an AWS Glue crawler to partition the source data
Features of Security Lake
If you need a place to manage your AWS security data, then Security Lake enables you to:
- Aggregate data: create a security data lake in your account to collect cloud, on-premises, and custom data sources across accounts and Regions
- Support various sources: access and centrally manage security logs and events from different technologies
- Transform and normalize data: make AWS service and third-party data compatible using the OCSF
- Provide multiple access levels: limit how subscribers can access and consume data in the data lake
- Manage multiple accounts and Regions: comply with data residency requirements by centrally enabling Security Lake across multiple Regions and AWS accounts
- Create customized configurations: specify sources, accounts, and Regions that need log collection
- Manage and optimize data lifecycle: customize retention settings and storage costs
Security Lake use cases
While Security Lake gives you a way to collect and store log and event data, you should understand the use cases and their limitations. Graylog offers a new input called “AWS Security Lake Input” that can be used to ingest these respective logs into Graylog for Security Analytics.
Security investigations
Security Lake aggregates, normalizes, and optimizes data storage so that security teams have all security-related logs and findings in a centralized location. However, it doesn’t give you a way to correlate and analyze the data.
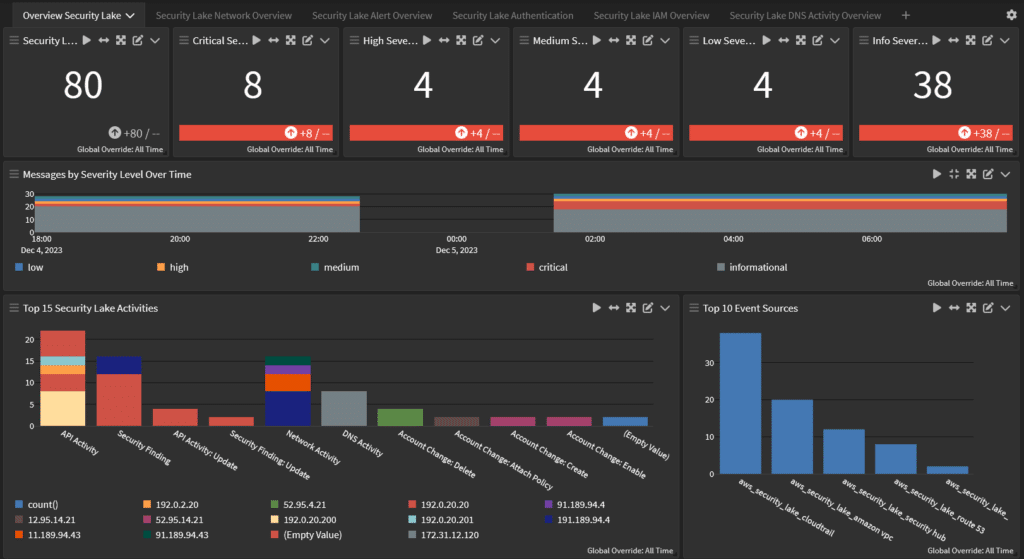
Compliance monitoring and reporting
You can use Security Lake to centralize data in one or more rollup Regions which makes it easier to do regional compliance and reporting. However, you still need to find a way to correlate and analyze the data to build effective reports.
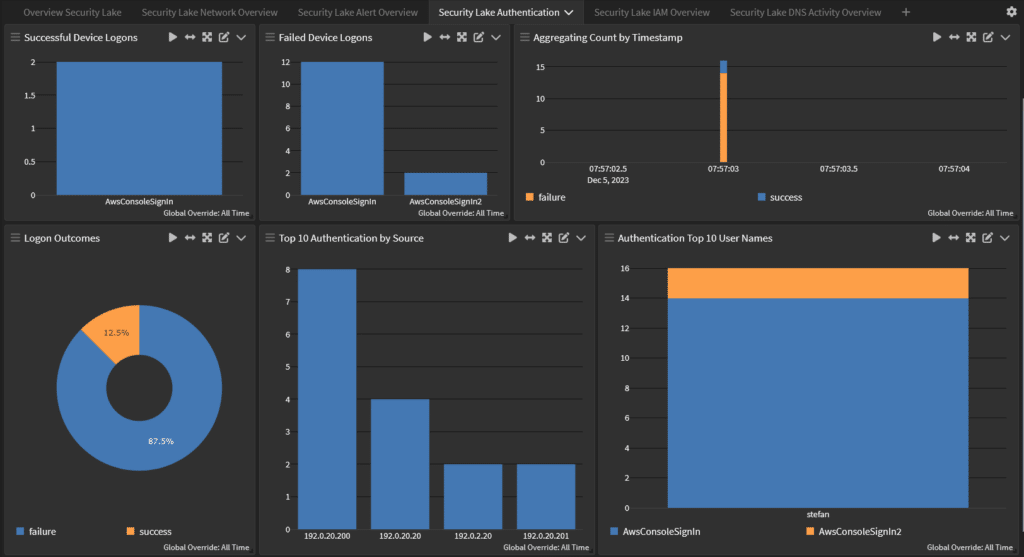
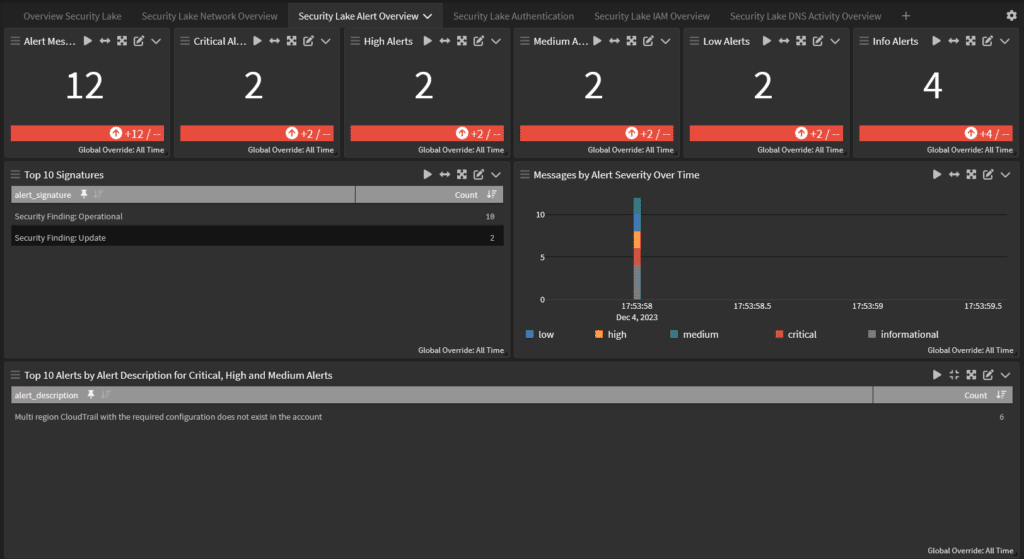
Security data management across hybrid environments
By storing security-related logs and data in Security Lake, you can better understand and respond to threats. However, while Security Lake simplifies the process of analyzing data, you still need analysis and automation solutions to make sense of the data, like identifying anomalies.
How to Optimize the Value of Amazon Security Lake
Amazon Security Lake gives you the ability to collect and store log and event data in a single location, enabling easier access and use. However, to optimize your Security Lake investment, you need a solution to correlate and analyze the data. To find the right solution for your organization, you should consider the following critical capabilities. Graylog offers features to enhance your data security analytics.
Correlation Engine
A correlation engine is the “under the hood” technology that compares events from the technologies generating the data, looking at when they happen and the order in which they happen. Utilizing Graylog Correlation Engine can help you identify security threats in Amazon Security Lake date. Some questions you should ask any vendor when considering their solution include:
- Can I perform per-field correlation so that I can get alerts for specific fields?
- How can I correlate events occurring across different sources to help identify patterns from multiple log sources?
- Can I look for negative events to see if some logs are missing?
- How can I build complex correlations that feed alerts back into the alert feed so that it can be used to chain alerts?
Dashboards
Dashboards give you a way to visualize your data so that you can make decisions faster. Since the correlation engine allows you to make sense of the aggregated data in your Security Lake, a Dashboard built on predefined searches gives you high-level insights into issues. Some questions you should ask any vendor when considering their solution include:
- How much domain knowledge do I need to create dashboards?
- How much domain knowledge do other people need to understand dashboards?
- What are the different types of visualizations I can use to communicate insights?
- How can I share dashboards?
- Can I maintain our organization’s access controls when sharing the dashboards?
Anomaly detection
You collect and aggregate this data so that you can gain insights. The correlation engine helps you connect the dots, but you still can’t manage creating baselines and detecting abnormal activity manually anymore. With more data at your fingertips, you can use machine learning (ML) for anomaly detection which automates the process of analyzing data and finding things that just don’t “look normal.” Some questions you should ask any vendor when considering their solution include:
- How much data science knowledge do I have to have to train and fine tune the ML?
- How much time does it take to add new datasets?
- How much background do I have to have to create custom use cases?
- Are there required data sources for this to work?
Graylog Security: The Correlation and Analysis Solution that Optimizes Security Lake’s Value
Graylog Security enables you to gain the full value of your Security Lake investment by providing analytics that helps you derive insights from the data. With Graylog Security, you get the correlation engine, dashboards, and anomaly detection that you need to create high-fidelity detections and rapidly investigate incidents.
By leveraging Graylog Security’s out-of-the-box content and security analytics, you can build high-fidelity alerts and then pivot directly into researching the log data that matters most. Our platform gives you all the functionality of a SIEM without the complexity, providing a robust technology that empowers users of all experience levels. See our documentation for information on this integration.
To see how Graylog Security makes cybersecurity investigations faster, contact us today.



