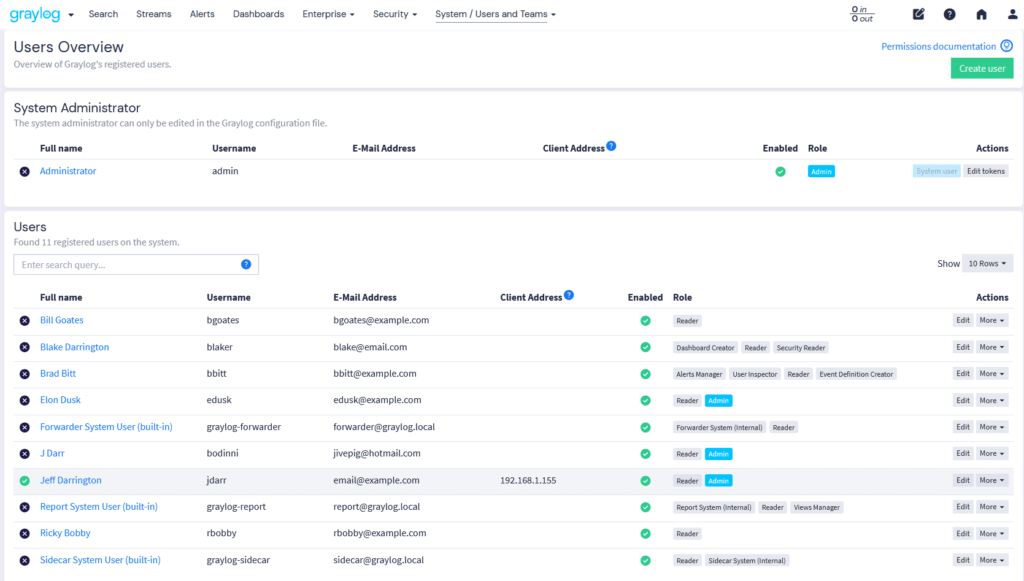
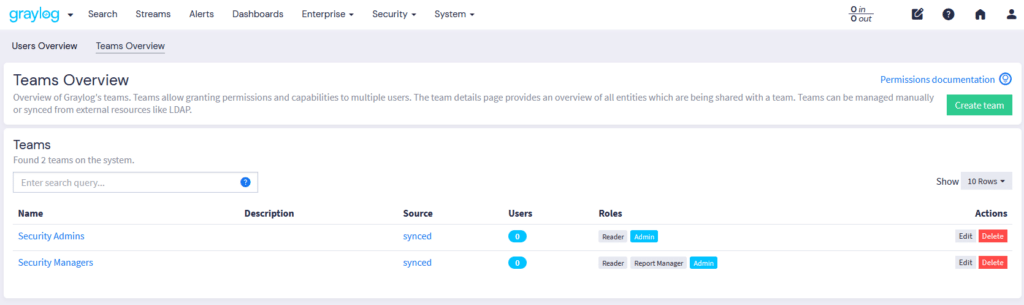
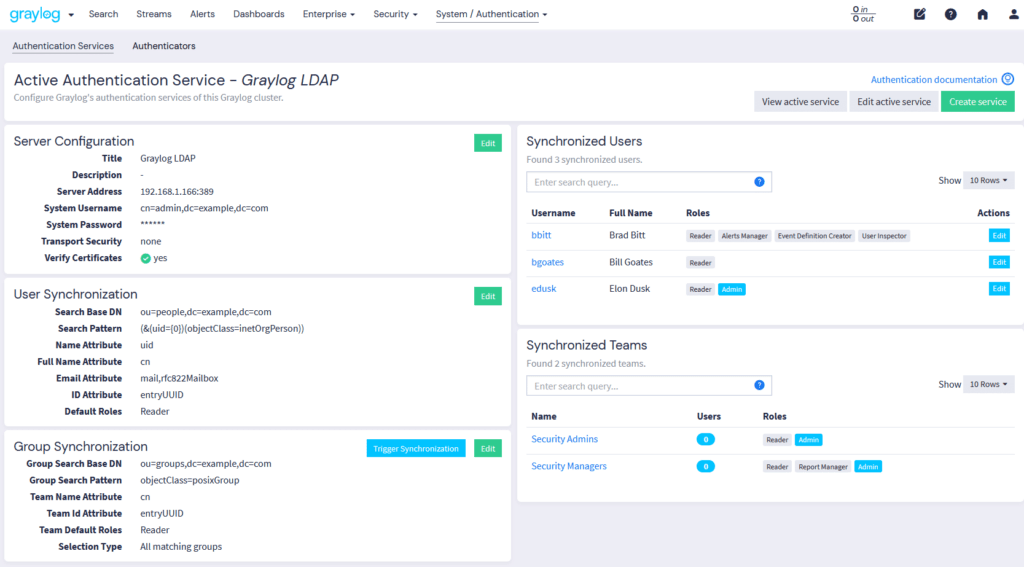
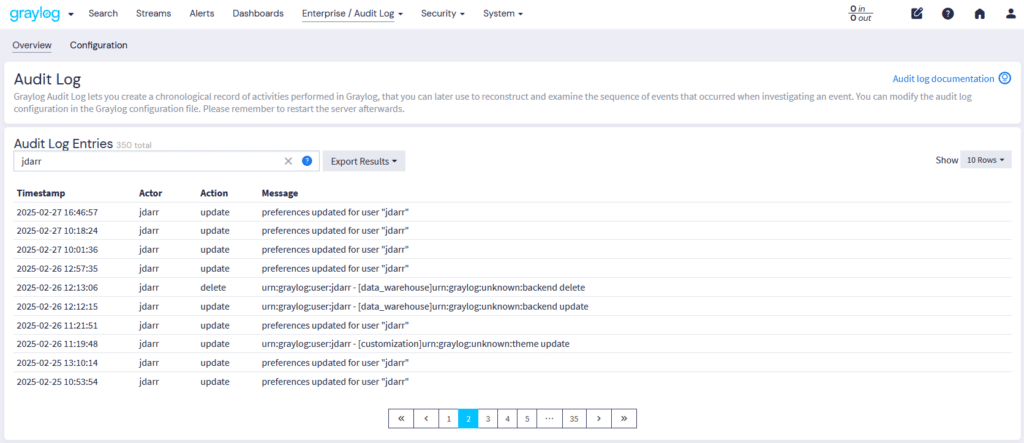
Together, access control and audit logs work in tandem to minimize security risks, prevent unauthorized access, and ensure operational integrity within the Graylog framework. By enforcing granular user permissions and maintaining a thorough record of all system activities, these features help organizations safeguard sensitive data, quickly detect anomalies, and streamline compliance with industry regulations such as SOC 2, GDPR, and HIPAA.