Organizations collect technologies like kids collecting baseball cards. As a company’s IT strategy matures, it adds new technologies to supplement previously existing ones, just like kids add new rookie cards to their collections of classics. While kids can leave their baseball cards randomly piled in a shoebox, organizations need to carefully identify and track their IT assets so that they can appropriately manage digital performance and cybersecurity.
Organizations can gain financial, operational, and security benefits with a robust IT asset management program.
What is IT asset management (ITAM)?
IT asset management (ITAM)consists of the policies, procedures, and technologies an organization uses to manage the costs and risks associated with technology assets throughout its lifetime. ITAM enables organizations to align business objectives with technology:
- Strategy
- Architecture
- Budget
- Procurement
Managing the IT asset lifecycle typically includes:
- Identifying hardware and software assets
- Building an inventory to track asset location and health
- Managing software licenses
- Determining when and how to retire assets
At a high level, an ITAM strategy enables organizations to:
- Enable cost-effective digital strategies, like managing cloud costs
- Streamline IT service management
- Document compliance activities
- Support cybersecurity monitoring
ITAM enables organizations to build cost-effective digital strategies and monitor data protection controls more efficiently.
What is an IT asset?
IT assets are the software and hardware that process, store, and transmit data to support the organization’s daily operations and workforce productivity.
Hardware assets include:
- Physical servers
- Workstations
- Mobile devices
- Laptops
- Keyboards
- Printers
- Network devices, like switches and routers
Software assets typically require a license or subscription and include the following:
- Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications
- Cloud-based systems and databases
- Installed software on user devices
What is the difference between IT asset management (ITAM) and IT service management (ITSM)?
While ITAM and ITSM respond to IT operations, they serve different purposes and focus on different aspects of IT management.
ITAM focuses on:
- Identifying and tracking devices, software licenses, applications, and other digital assets across their lifetimes
- Maintaining an IT asset inventory, including information, location, status, and usage
- Ensuring optimization, security, and compliance
- Managing IT assets financials, like cost of ownership, maintenance, and risk
ITSM focuses on:
- Managing and delivering IT services to users or customers, like incident, problem, and change management
- Establishing and maintaining service level agreements (SLA) to provide a framework for effective incident response and change management
- Delivering IT services to users or customers so they can accomplish business objectives
Without a strong ITAM, the ITSM function cannot work effectively and efficiently. ITSM relies on the accurate and up-to-date information that the ITAM provides.
How does an IT asset management process work?
Implementing a systematic ITAM process enables you to effectively identify and manage IT assets to improve visibility, control, security, compliance, and financial management.
Discover assets
Before you can manage your assets, you need to identify what you have. Often, this process incorporates scanning networks to identify all connected devices.
Identify asset owners
Every asset has someone responsible for maintaining it. For example, a workforce member is responsible for a laptop, while a department head may be responsible for a SaaS subscription.
Calculate life cycle costs
Across every IT asset’s lifecycle, you should identify the various costs associated with it, including:
- Upfront fees
- Depreciations
- Maintenance
- Subscription or license renewals
- Disposal
Establishing and tracking metrics
To determine whether you’re effectively managing your hardware and software metrics, you need to set and track key performance indicators (KPIs). Some typical metrics include:
- Number of IT assets
- Underutilized licenses
- Overutilized licenses
- Maintenance costs
- Licensed software
- Software subscriptions
- Unlicensed software
- Expired warranties
Track maintenance activities
Change management and maintenance activities should be part of your ITAM processes. Your change management process defines responsibility for activities that support:
- Software updates
- Configuration changes
- Deployment processes
- Service validation and testing
- Transition planning and support
Monitor asset locations and access
Asset location tracking includes knowing both:
- Physical location, like office branch
- Network location, like public or subnet
Additionally, when you can track the locations, you can track who has access to the assets, including:
- Physical: building address and keycard access
- Digital: limited do appropriate job function needs
Manage End-of-Service/End-of-Life
Every IT asset’s usefulness comes to an end. In some cases, you may decide to terminate a subscription. Employees may need to return physical devices to the IT department. Regardless of whether the asset is hardware or software, your ITAM process should include the following:
- When to retire an asset
- How to handle data
- How to dispose of the asset
What are the stages of an IT asset’s lifecycle?
Most IT assets follow a similar lifecycle pattern that starts before the organization makes the purchase and ends when the organization finally retires the asset.
Typically, the stages look like this:
- Procurement: Research, risk assessment, contract negotiations
- Deployment: Setting up and configuring hardware devices, installing software, granting access to SaaS applications, integrating into the existing IT infrastructure
- Monitoring and maintenance: Monitoring health and availability, applying version updates, installing patches
- Utilization and optimization: Analyzing usage data to optimize asset allocation, improve efficiency, and make data-driven purchasing decisions
- Upgrade and retirement: Identifying when to upgrade or replace assets, migrating data, securely disposing of assets, updating documentation and inventory
- Disposal or disposition: Erasing data from devices, recycling or disposing of hardware components in compliance with environmental regulations, disposing of or storing data as required by regulatory or compliance requirement
What are the benefits of ITAM?
Implementing asset management processes gives you various financial, operational, security, and compliance benefits.
Optimize costs
When you have insight into all digital assets, you gain visibility into how people use them. With this information, you can determine how to refocus your spending by:
- Eliminating licenses
- Reducing subscription costs
- Scaling back resources
- Evaluating performance
Improve efficiency
When you have all IT asset information stored in a central location, your IT operations team can more efficiently respond to requests because they have rapid access to:
- Asset location and configuration
- SaaS user data
- Operating system versioning
Enhance decision-making
When you manage IT assets purposefully, you can make informed decisions because you gain insight into:
- Asset performance
- Usage trends
- Compliance status
Mature security
You can’t protect what you don’t know you own. IT asset inventories build the foundation of your security program by providing insight into locations that process, store, transmit, and collect sensitive data. Further, when you have a robust ITAM program, you identify the people responsible for managing those devices, networks, applications, and storage locations.
Streamline compliance
Most data protection compliance mandates require organizations to have an IT asset inventory. As part of ITAM, you document all hardware and software data, including the people responsible for managing it.
Reduce audit costs
By aggregating all ITAM data in a single location, you reduce the time it takes to gather audit documentation and respond to follow-up questions.
Centralized Log Management for IT Asset Management
Your centralized log management solution aggregates and analyzes logs from digital assets across your IT infrastructure. By consolidating all data in a single location, your security, and IT operations teams have a shared view of asset performance and control effectiveness.
Unified view with real-time monitoring
Every IT asset generates log data, giving you real-time information about what it’s doing. When you aggregate this into a centralized log management solution, you gain comprehensive visibility into all devices, applications, and services.
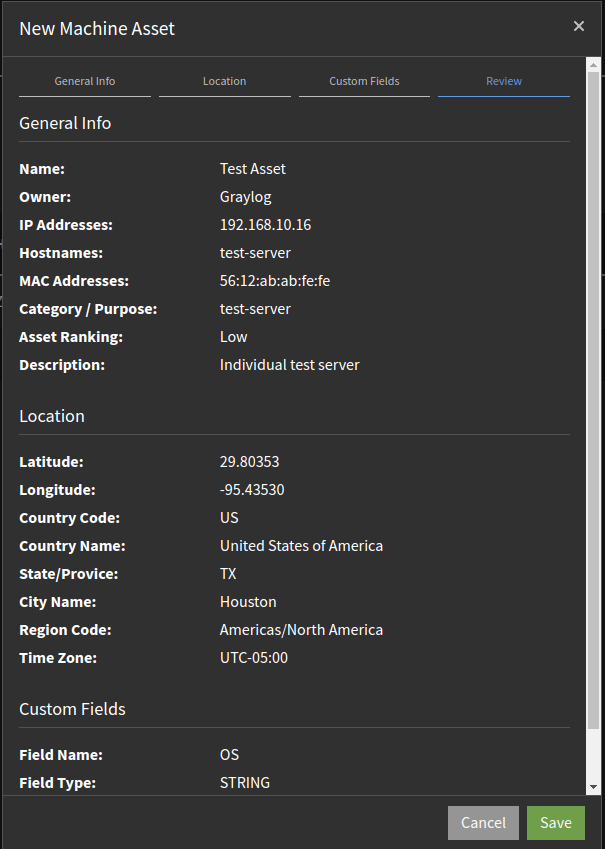
For example, you can use that data to build a database that includes:
- Assets
- Hostnames
- MAC addresses
With a centralized log management solution that enriches log data, you can also incorporate the following:
- Geographic location
- Hostname history, including past IP addresses over time, wireless networking cards, and physical cards
By correlating this data, you can identify critical assets more effectively, enabling a more robust ITAM.
Streamlined maintenance and service management
When managing your IT assets efficiently, you can engage in proactive maintenance activities and improve your service management processes. With visibility into usage, you can identify issues before they impact users or customers, reducing the number of calls to your service desk.
Centralized log management enables actionable and scalable system health and performance data observability. You can take a proactive approach to maintenance by creating a custom set of rules that trigger responses to prevent a minor issue from becoming more severe.
When a customer contacts your service team, centralized log management enables faster, streamlined root cause analysis. By reducing the time issue troubleshooting and resolution take, you minimize operational impact.
Security and compliance
Similarly, centralized log management enables your security teams to monitor for, detect, investigate, and respond to security incidents more efficiently and effectively. When you can use your centralized log management solution’s data to identify critical IT assets, you can focus your security monitoring activities more efficiently.
With a shared, single-source-of-data, your security and IT operations teams can collaborate more effectively so that you can reduce key metrics like:
- Mean time to detect (MTTD)
- Mean time to investigate (MTTI)
- Mean time to recover (MTTR)
Data-driven decision-making
When you can create custom dashboards in your centralized log management solution, you can use them to identify trends, patterns, and usage statistics. Leveraging this data, you can make informed decisions that optimize asset lifecycle management and reduce the overall total cost of ownership (TCO).
Graylog Security: Centralized Log Management for ITAM
With Graylog Security, organizations can import their IT asset information directly into our platform, giving them a way to further enrich their log data. With the ability to correlate assets and security monitoring data, IT and security teams can investigate incidents faster, identifying the device or software causing an issue.
Purpose-built for modern log analytics, Graylog removes complexity from your daily activities, giving you the real-time log view you need that ensures continued availability and streamlines investigations. Using Graylog Cloud Platform, you can maximize the value of your resources, getting the flexibility needed to add new data sources, processing rules, search templates, alerts, visualizations, reports, and unlimited users.
To get an overview of Graylog, including a 20-minute in-depth demo and 10-minute Q&A session, contact us today.