Wherever you live, people can find you using either a street address or a set of latitude and longitude numbers. In the digital world, your website’s domain name or URL is the street address while the IP address is the latitude and longitude. For example, it would be cumbersome to tell people that you live at 35°05′17″N 109°48′23″W, but easy to say a number and street name.
IP address data is useful for both protective and detective cybersecurity functions. You can use it to help identify a user’s devices or to prevent potentially harmful incoming communications by using a known malicious range. By understanding how IP lookup data can improve cybersecurity, you can incorporate it into your controls and detections.
Understanding Domain IP Lookup
The domain IP lookup process helps identify malicious web traffic by uncovering the IP address associated with a domain name to gain insight into:
- Hosting details
- Geographic location
- Potential security vulnerabilities
- Timezone information
Since IP addresses are often key indicators of compromise (IoCs), organizations should ensure that they have accurate IP address lookup data. In some cases, geolocation data from free databases can be outdated or imprecise.
How does domain IP lookup contribute to cybersecurity?
Domain IP address lookup supports key security initiatives like identifying:
- Phishing attacks: insight into the geographic location and host for malicious emails
- Malware infections: visibility into command and control (C2) server communications
- Risky IP addresses: sites users visit that could deliver malware
- Unauthorized access: location of device connecting to the network
IP lookup supports these cybersecurity initiatives through:
- Verification: Confirming a website domain name’s authenticity
- Threat identification: Flagging potentially malicious IP addresses
- Prevention: Blocking users from accessing risky websites
What Data Can You Gather Using an IP Lookup Tool?
IP lookup tools provide critical, detailed information that organizations can use to improve their cybersecurity risk management and monitoring.
IP Address Validity
An IP WHOIS lookup can provide details about an IP address, including its:
- Country
- City
- State
- Internet service provider
- Operating system
- Browser
This data can provide insight into cybersecurity threats like:
- Phishing
- Data leaks
- Fraud
Blocklist Checks
To mitigate risks and support Allowable Use Policies (AUPs), organizations often create block lists that prevent users from accessing known risky domains or categories of websites. IP lookup tools perform blocklist checks to identify websites with negative reputations, like ones associated with spam.
Proxy Server Detection
Proxy server detection enables you to identify users trying to conceal their IP addresses using a proxy, VPN, or Tor browser. Despite the legitimate use cases, malicious actors often use these technologies as part of their attack activities, like when engaging in the reconnaissance phase. With IP geolocation tools, you can identify and restrict this risky access by allowing listing authorized VPNs.
IP Hostname and Domain
Insight into domain names and their hosting locations can assist threat analysis by connecting web traffic to its origin. Linking a public IP address to the internet service provider aids in detecting suspicious activity.
Geolocation
IP geolocation data provides insight into a connection’s:
- City or country of origin
- ISP Details
- Latitude and longitude coordinates
For organizations, this data can help:
- Mitigate fraud by connecting a device location to billing details
- Trace Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack locations
WHOIS Information
The WHOIS protocol is a global system for querying databases and identifying IP address ownership, managed by the following regional internet registries:
- African Network Information Centre (AFRINIC)
- American Registry for Internet Numbers (ARIN)
- Asia Pacific Network Information Centre (APNIC)
- Latin America and Caribbean Network Information Centre (LACNIC)
- Réseaux IP Européens Network Coordination Centre (RIPE NCC)
WHOIS information confirms geolocation data, so identifying discrepancies can help enrich security threat detection data.
Open Port Scan
Using IP lookup tools across different applications can provide insight into open-ports and potentially at-risk servers. Malicious actors often scan for open ports as part of an attack’s reconnaissance phase. With IP lookup data, you can identify potentially malicious connections that help mitigate attack risk.
7 Ways to Improve Cybersecurity with IP Lookup and Geolocation Data
By using IP address data, you can proactively manage risks, verify user authenticity, and improve their threat detection capabilities.
1. Blocking Traffic from High-Risk Locations
Blocking inbound traffic from high-risk locations enables you to mitigate:
- DDoS attacks: Restricting the number of incoming requests from suspicious locations can help against botnets trying to overwhelm servers.
- Data loss: Preventing communications from high-risk locations limits attackers’ ability to send requests to infected devices and resources that would lead to data exfiltration.
- Unauthorized access: Blocking inbound access from risky domains and locations can act as another layer of defense.
As a best practice, you should consider blocking:
- Malformed DNS queries or non-DNS traffic attempting to reach ports typically associated with DNS traffic
- Newly Registered and Observed Domains (NROD) category of IP addresses
- Categories of domains that have no business use case, like gambling sites
2. Geolocation-Based Authentication
You can incorporate users’ geographic location as additional information when creating Attribute-Based Access Controls (ABAC) to trigger additional verification when detecting an unusual location, like requiring multi-factor authentication (MFA). By adding geolocation data to firewall, intrusion detection systems (IDS), or intrusion prevention systems (IPS), you can improve detections for potential unauthorized access attempts.
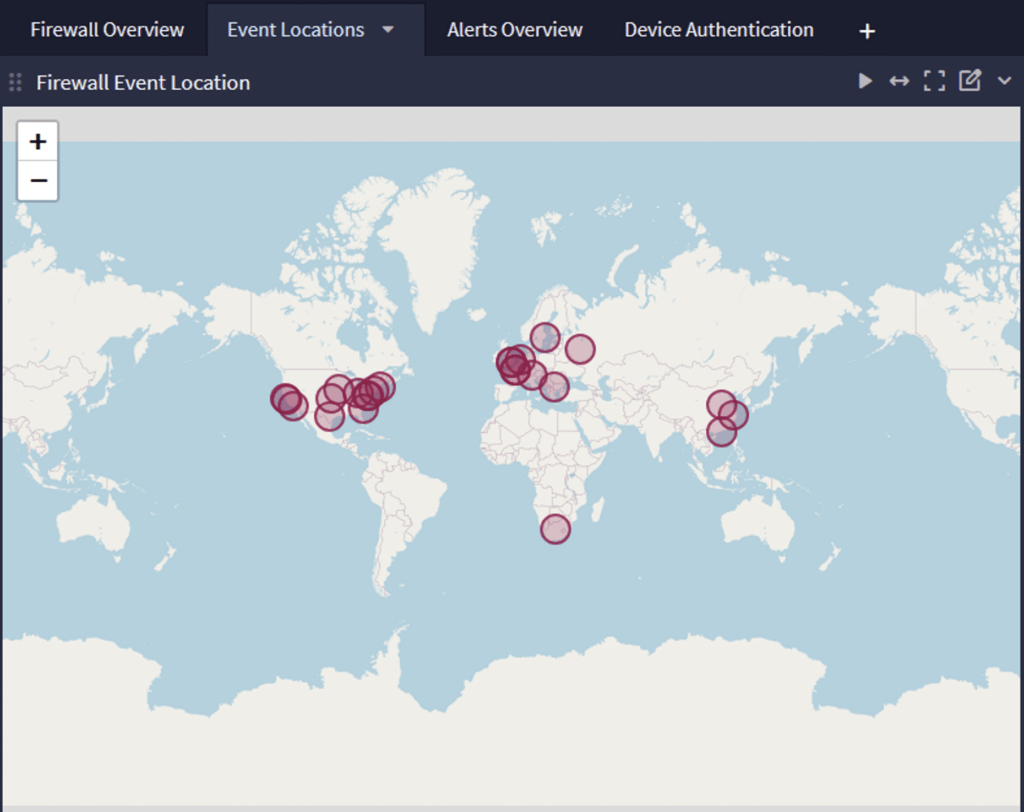
3. Geo-Fencing Critical Systems
Geo-fencing creates virtual boundaries around systems by only allowing access from trusted geographic areas. By creating allow lists for authorized IP addresses, you can limit access to critical databases and infrastructure. However, you should remember that for most systems, this creates a resource access and availability problem, so use it strategically.
4. Monitoring for Suspicious Activity
Incorporating IP address information into detections and alerts can help identify anomalous activity, like:
- Assets traveling outside an assigned region
- Unfamiliar incoming IP connections that might signal a request from a malicious device or actor
- Abnormal outgoing communications that might indicate data exfiltration activities
For example, if your firewall rulesets include IP lookup and geolocation data, you can incorporate these attributes in Sigma rules as part of your continuous monitoring and threat hunting activities.
5. Location-Specific Rate Limiting
Applying rate-limiting rules based on geolocation can mitigate the risks of DDoS and brute force attacks. Controlling the number of requests from high-risk regions helps you mitigate risks related to high-volume requests and automated activities that can lead to a security incident. As the threat landscape evolves, you should evaluate and adjust threat detections to reflect threat intelligence and newly identified malicious IPs.
6. Implementing VPN Restrictions
When investigating and responding to incidents, understanding the relationship between the organization’s IP addresses and its VPN allow lists is critical. To protect internal resources from unauthorized access, you should consider:
- Allowing access only essential company VPN IP addresses
- Blocking access from all other VPN IP addresses
7. IP Reputation Management
IP reputation management involves assessing the risks associated with specific IP addresses using market insights and numerous queries. Automated tools assign reputation scores to IPs, which help organizations identify high-risk IPs based on historical behaviors. Incorporating this data into your threat detections can improve alert fidelity and enhance monitoring.
Graylog Security: High-Fidelity Detections and Alerts with Correlated Security Data
With Graylog’s security analytics and anomaly detection capabilities, you get the cybersecurity platform you need without the complexity that makes your team’s job harder. With our powerful, lightning-fast features and intuitive user interface, you can lower your labor costs while reducing alert fatigue and getting the answers you need – quickly.
Our prebuilt search templates, dashboards, correlated alerts, and dynamic look-up tables enable you to get immediate value from your logs while empowering your security team.
For more information about how Graylog Security can help you achieve your NIST CSF 2.0 objectives, contact us today.