Everyone has a story about that one road trip where traffic got backed up, making people late to the event. When you have network connectivity problems, your information highway gets clogged up, making it difficult for users to access resources efficiently.
While network troubleshooting strategies may seem simple, a lot of nuance and complexity lies in the activities when you dig into your data. Connectivity issues can come from various sources, and they have a wide-ranging impact across internal operations, customer experience, and overall productivity.
By learning the types of problems and how to diagnose them, you can troubleshoot network issues more rapidly. Many tools like Wireshark can be used to help troubleshoot network issues. Central Log Management is Important when identifying application failures, slow web response times, and many other erratic behaviors on the network.
What Is Troubleshooting a Network?
Troubleshooting network issues takes a systematic approach to:
- Identifying and resolving connectivity issues
- Ensuring optimal network performance
- Providing seamless network access
Network, IT, and security teams often collaborate when troubleshooting a network problem because the underlying issues can come from:
- Device hardware
- Software or firmware issues
- Cyber attacks
By documenting each step in the evaluation and resolution process, you can meet compliance requirements and, hopefully, prevent the same problem from happening again.
What Impact do Network Connectivity Issues Have on Businesses?
Network connectivity issues can disrupt business operations by preventing workforce members or customers from accessing resources. These disruptions often lead to:
- Lost productivity: Unable to connect to applications or files required to perform job functions
- Preventing collaboration: Inability to use cloud-based collaboration tools, like messaging applications
- Lost revenue: Interruption of transactions can cause financial issues, like customer church or business disruption
- Customer dissatisfaction: Inability to access services undermines customer trust and loyalty
What are the Types of Network Issues?
Understanding the various types of network issues can act as a good starting point for investigating them and improving your network’s reliability.
1. Hardware Issues
Hardware issues can lead to connectivity difficulties, performance degradation, and network outages. They often arise from device misconfigurations or hardware failures. Common problems include:
- Overheating components
- Low battery status
- Damaged cables
To maintain your network, you should regularly review the configuration of routers, switches, and cables.
2. Software Issues
Software conflicts resulting from outdated operating systems, software, or firmware can make applications incompatible. Some ways to prevent these problems include:
- Regularly updating operating systems, software, and firmware
- Scanning for vulnerabilities
- Monitoring network traffic
- Reviewing system logs
3. Bandwidth Issues
Bandwidth limitations can cause network congestion, slow speeds, and increased latency. High-bandwidth activities can overload the network. For example, downloading large files or streaming videos during peak times can slow down the network.
Some ways to prevent these problems include:
- Regular monitoring and configuring of network devices
- Proper bandwidth allocation and utilization
4. Configuration Issues
Misconfigured network devices or software can lead to performance bottlenecks and prevent access to external networks. For example, incorrect IP addressing can create connectivity issues. Regularly reviewing and updating configuration files can mitigate these issues.
5. Firewall and IP Management Issues
Misconfigured firewalls or conflicting security policies can block legitimate network traffic, leading to connectivity issues. However, overly permissive rules or outdated firewall software can expose the network to vulnerabilities, potentially leading to a data breach. For example, bloated firewall rulesets can mean that the device or application takes more time to scan traffic, slowing down the network.
Some ways to prevent these problems include:
- Regularly reviewing firewall configurations
- Optimizing rulesets
- Deleting shadowed or unused rules
6. Security Incidents
Security incidents can impact network performance in several ways. For example, a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack floods the web server with too many requests which impacts both the server’s availability and the bandwidth on the server’s network. Additionally, security incidents that include data theft may slow down networks as attackers download high volumes of data.
Some ways to mitigate these risks include:
- Monitoring networks for abnormal activity
- Monitoring user account data to identify anomalies
- Requiring multi-factor authentication (MFA) prior to granting network access
5 Network Troubleshooting Best Practices
In complex, connected IT environments, troubleshooting network issues can feel overwhelming. For example, when someone calls the help desk to report that an application isn’t functioning right, investigating the problem can feel overwhelming since it could come from the following:
- Web server where the application resides
- Database that application uses
- Network segment
1. Centralize Logs
Your logs give you information about activities across your environment. Every device and technology generates logs, so collecting the information in a single location allows you to correlate issues that make your investigation faster. Some locations that you should consider collecting logs from include:
- Hubs
- Switches
- Routers
- Bridges
- Gateways
- Modems
- Repeaters
- Access Points
- Firewalls
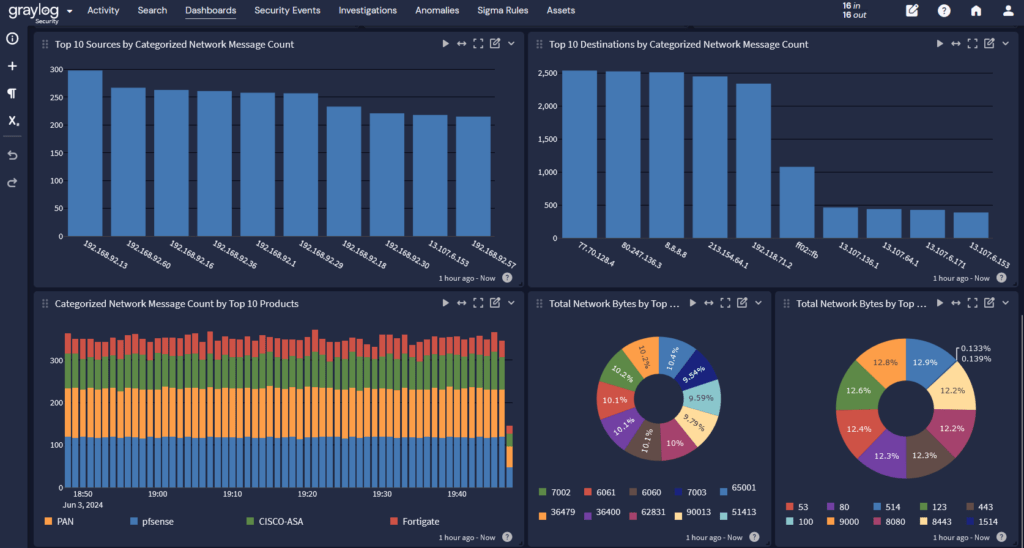
2. Create Dashboards
With all log data in a single location, you can create dashboards that make it easier to gain visibility into what’s happening across your environment. For example, you can correlate information from your network devices, firewalls, and user logins to understand how people are using your network and what abnormal behavior looks like. These dashboards make it easier for you to start an investigation by helping narrow down where the problem lies.
3. Create Alerts
Part of creating dashboards is high-level visibility. The other half is getting the information available to create alerts that drive investigations across IT and security issues. Since many different factors can lead to a network issue, high-fidelity alerts that make it easier to distinguish between events like software conflicts and DDoS attacks can help you get the network up and running faster.
4. Conduct Regular Audits
When you regularly audit your network security settings and configurations, you can mitigate network outage risks. Whenever you make changes to the settings and configurations, you should document them because changes can disrupt service, giving you a potential starting point for your investigation.
5. Adhere to an Escalation Framework
An escalation framework enables you to direct problems to the appropriate expertise levels. For example, you can use the Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) version 4 framework practices for incident management to create different tiers of service. Tier 1 troubleshooting may handle basic issues, while more complex network problems require people with more experience who can provide advanced intervention.
Graylog Enterprise and Security: Comprehensive Network Insights for Troubleshooting Network Issues
Graylog Enterprise makes it easier for you to navigate through your data and respond to network issues faster. With Graylog Enterprise, you can accelerate quick problem identification and resolution while improving collaboration across different internal teams.
When you need comprehensive insights into your security posture, Graylog Security has you covered. As the only security information and event management (SIEM)/threat detection and incident response (TDIR) platform with native data routing, tiering, and archiving in a single technology, you can level up your security capabilities to identify network-based attacks faster.