The financial services industry has been a threat actor target since before digital transformation was even a term. Further, the financial services organizations find themselves continuously under scrutiny. As members of a highly regulated industry, these companies need to comply with various laws to ensure that they effectively protect sensitive data.
The adoption of the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) places additional resilience compliance requirements on the European financial sector, ones that centralized log management can help them manage.
What is the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA)?
Formally adopted by the European Parliament and goes into effect on January 17, 2025, the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) established uniform network and information system security requirements across the financial sector and the third-parties that provide Information Communication Technology (ICT) services, including cloud platforms and data analytics services.
The DORA regulatory framework requires organizations to make sure they can withstand, respond to, and recover from ICT-related disruptions and threats. It sets out standardized requirements for preventing and mitigating cyber threats across all European Union (EU) member states.
Who will DORA apply to?
To achieve DORA’s resilience goals, the regulation applies to a long list of entities within the financial services industry and third-parties that enable them, including:
- Credit institutions
- Payment institutions
- Account information service providers
- Electronic money institutions
- Investment firms
- Crypto-asset services providers
- Central security depositories
- Central counterparties
- Trading venues and repositories
- Managers of alternate investment funds
- Management companies
- Data reporting service providers
- Insurance and reinsurance undertakings
- Insurance, reinsurance, and ancillary insurance intermediaries
- Institutions for occupational retirement provision
- Credit rating agencies
- Administrators of critical benchmarks
- Crowdfunding service providers
- Securitisation repositories
- ICT third-party service providers
What are DORA’s key provisions?
Section II outlines DORA’s key requirements including:
- Article 6 ICT risk management framework: strategies, policies, procedures, ICT protocols and tools necessary to protect information and ICT assets
- Article 7 ICT systems, protocols and tools: use and maintain updated ICT systems, protocols and tools that are appropriate to operational magnitude, reliable, equipped with sufficient capacity, and technologically resilient
- Article 8 Identification: identify, classify, document, and engage in a risk analysis for all information and ICT assets and processes, including those on remote sites, network resources, and hardware equipment
- Article 9 Protection and prevention: develop, document, implement, and maintain security policies and technical controls that protect data confidentiality, integrity, availability, and authenticity and continuously monitor the effectiveness of controls
- Article 10 Detection: implement mechanisms and provide sufficient resources to monitor and detect, across multiple layers of control, anomalous activity by using defined thresholds and criteria that trigger and initiate incident response processes
- Article 11 Response and recovery: establish and implement an ICT business continuity policy based on a business impact analysis (BIA) that includes dedicated, appropriate, documented, and tested arrangements, plans, procedures, and mechanisms for ensuring critical functions, responding to and resolving incidents, enable incident containment, estimate preliminary impact, damage, and losses, and establish communications and crisis management activities
- Article 12 Backup policies and procedures, restoration and recovery procedures and methods: develop, document, implement and test backup, restoration, and recovery policies, procedures, methods, and service level agreements that can be activated without jeopardizing network ir information system security or data availability, authenticity, integrity, or confidentiality
- Article 13 Learning and evolving: implement capabilities and staff to gather vulnerability and cyber threat information, develop ICT-security awareness programs, and review incident detection, response, forensic analysis, escalation, and internal and external communication capabilities to improve business continuity
- Article 14 Communication: implement crisis communications plans and policies that inform internal staff and external stakeholders about ICT-related incidents or vulnerabilities
For small and non-interconnected investment firms, payment institutions, electronic money institutions, and occupational retirement provisions, or other exempt entities, Article 16 articulates a simplified ICT risk management framework that requires:
- Implementing and maintaining an ICT risk management framework with mechanisms and measures that mitigate risk
- Continuously monitoring ICT system security and functioning
- Protecting data availability, authenticity, integrity, and confidentiality using sound, resilient, and updated ICT systems, protocols, and tools
- Promptly identifying and detecting ICT-related risks, incidents, and anomalous activities
- Identifying key ICT third-party service provider dependencies
- Implementing business continuity plans, response, and recovery measures, including backup and restoration
- Testing risk mitigation measures, data protections, and business continuity plans
- Implementing changes based on tests and post-incident analyses, including changes to ICT risk profile, ICT security awareness programs, and staff and management digital operational resilience training
The Regulatory Technical Standards
On January 17, 2024, the final draft of the Regulatory Technical Standards was published. Under Section V ICT Operations Security, Article 12 Logging defines acceptable procedures, protocols, and tools.
The logging procedures and protocols should:
- Identify the events to log
- Retain logs for an appropriate time
- Enable the secure handling of log data
When using logs to detect anomalous activities, organizations are required to collect log events related to the following:
- Identity and access, including logical and physical access control
- Capacity management
- Change management
- ICT operations, including system activities
- Network traffic, including performance
The details captured in the logs should align with their purpose and usage to enable accurate alerting and forensic analysis. Under Chapter III, Article 23 organizations shall implement detection mechanisms allowing them to:
- Collect, monitor, and analyze internal and external factors, including logs collected according to Article 12
- Generate alerts for identifying anomalous activities and behaviors with automated alerts based on predefined rules
- Prioritize alerts to manage incidents within the required timeframe
- Record, analyze, and evaluate relevant information on all abnormal activities and behaviors either automatically or manually
When establishing criteria that triggers threat detection and incident response (TDIR), organizations shall consider the following criteria:
- Indications that malicious actors carried out malicious activity or compromised a system or network
- Data losses detected that impact data availability, authenticity, integrity, and confidentiality
- Adverse impact on transactions and operations detected
- System and network unavailability
Compliance Monitoring For DORA Compliance
Centralized log management with security analytics enables you to continuously monitor your environment and create high-fidelity alerts that enable faster response, investigation, and recovery. To help you meet DORA compliance requirements, you can use your centralized log management solution to support:
- Access monitoring
- Network monitoring
- Endpoint security
- Patch management
- Data exfiltration/data loss
- Incident and response
Further, it enables many of DORA’s key requirements, including:
- Threat hunting
- Detection with high-fidelity alerts
- Remediation of vulnerabilities
- Incident investigation
Access Monitoring
Your centralized log management solution ingests access logs from across your environment, including on-premises and cloud-based resources. When paired with user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA), it gives you a robust access monitoring solution to detect and investigate anomalous behavior, even within a complex environment.
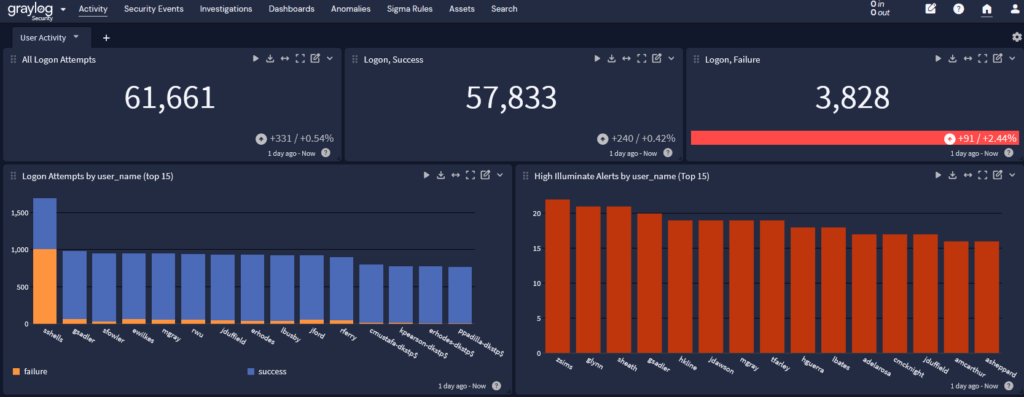
By using a centralized log management solution with security analytics, you can engage in security functions like:
- Privileged access management (PAM)
- Password policy compliance
- Abnormal privilege escalation
- Time spent accessing a resource
- Brute force attack detection
Network Monitoring
When monitoring network security, you’re usually correlating and analyzing data from several different tools.
Your firewalls define the inbound and outbound traffic, giving you the ability to detect suspicious activity like data traveling to a cybercriminal-controlled server.
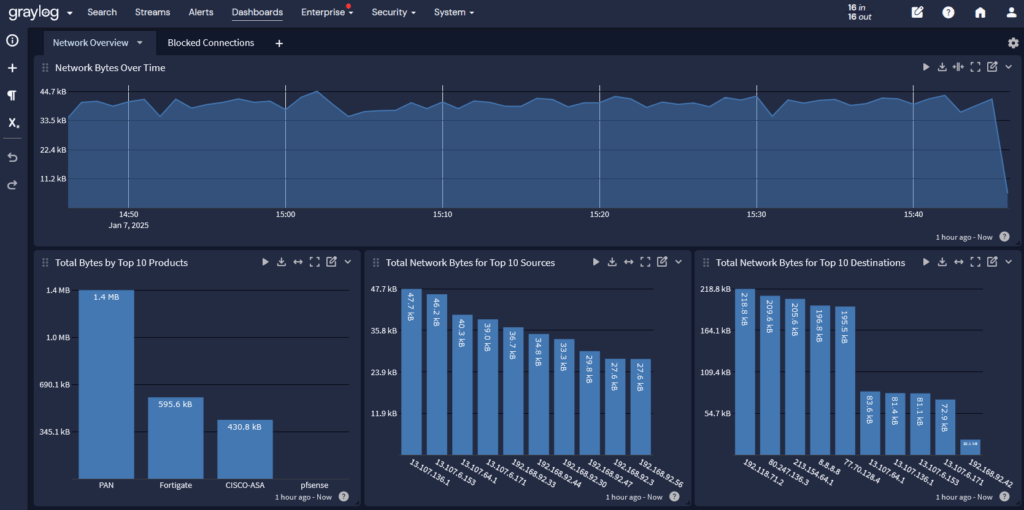
Intrusion detection systems and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) provide visibility into potential evasion techniques. When combined with your firewall data, you have a more complete story.
When the centralized log management solution also incorporates security analytics, you can set baselines for normal network traffic that help you detect anomalies for visibility into a potential security incident.
Data exfiltration
Between credential-based attacks, malware/ransomware attacks, and Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs), monitoring your systems for data exfiltration is critical to DORA compliance.
If your centralized log management solution provides security analytics that you can combine with threat intelligence, your dashboards and high-fidelity alerts enable you to more rapidly detect, investigate, and respond to security incidents.
For example, when you can aggregate your network monitoring and antivirus logs then correlate them with UEBA to detect anomalies, you can create alerts that provide insights into abnormal data downloads indicating a security incident.
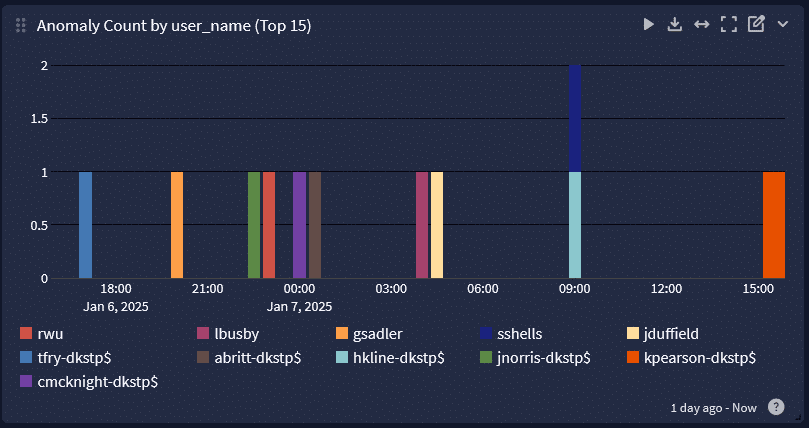
Incident response and automated threat hunting
With lightning fast search and proactive threat hunting capabilities, you can implement a robust incident response plan that enables digital resilience.
For example, if you can create queries using parameters instead of specific values, you can optimize search for real-time answers.
To take a proactive approach, you can create parameterized searches that look for advanced threat activities like:
- Abnormal user access to sensitive information
- Abnormal time of day and location of access
- High volumes of files accessed
- Higher than normal CPU, memory, or disk utilization
- Higher than normal network traffic
Compliance reporting and post-incident learning
Your senior leadership team needs to know what happened and how quickly you responded, but it may not need the deep technical details. Your centralized log management solutions dashboards can provide the high level visualizations that enable everyone to evaluate the security incident after you restore and recover your systems.
For example, you could use a dashboard to show:
- Start of incident: when logs documented changes
- Incident activities: what types of changes the logs documented to highlight what the threat actor tried to do
- Containment/Eradication: when logs stop reporting the activities indicating the threat actor is no longer acting in the system
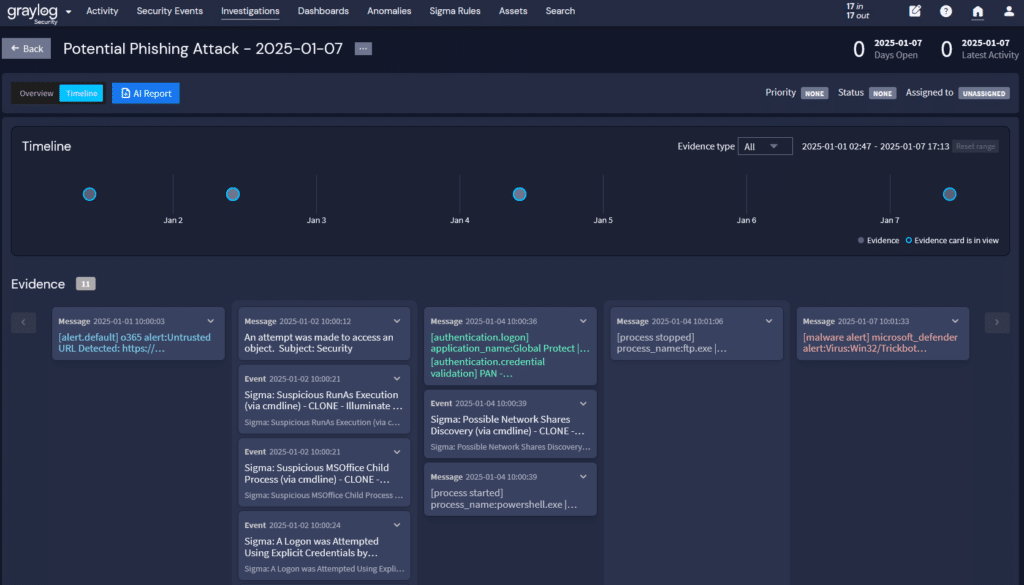
Graylog Security: Security analytics without complexity
With Graylog security analytics and anomaly detection capabilities, you get the cybersecurity platform you need without the complexity that makes your team’s job harder. With our powerful, lightning-fast features and intuitive user interface, you can lower your labor costs while reducing alert fatigue and getting the answers you need – quickly.
Our prebuilt search templates, dashboards, correlated alerts, and dynamic look-up tables enable you to get immediate value from your logs while empowering your security team.
For more information about how Graylog Security can help you comply with DORA, contact us today.